Welcome to Promuscle Club! If you’re on a journey to build muscle, you’ve likely heard about the importance of protein. But how much do you really need? What types are best? When should you consume it? This guide will answer all these questions and more. Let’s dive into the ultimate guide to protein intake for muscle growth.
Why Protein Matters for Muscle Growth
Proteins are the building blocks of muscle. They are composed of amino acids that repair and build new muscle fibers after they are damaged during intense workouts. Without adequate protein intake, your muscles won’t have the necessary resources to grow bigger and stronger.
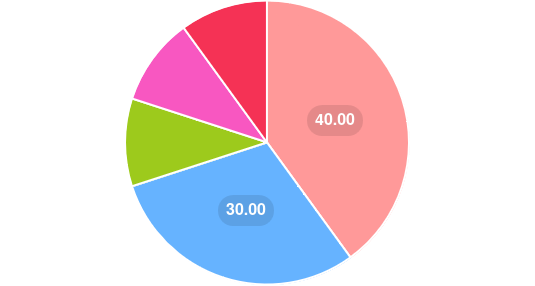
Here’s a pie chart illustrating the various reasons why protein is essential for muscle growth:
- Building Muscle Fibers: 40%
- Repairing Muscle Damage: 30%
- Energy Source: 10%
- Hormone Production: 10%
- Enzyme Functions: 10%
This visual representation emphasizes the primary roles of protein in muscle development and maintenance.
Benefits of protein
Protein is an essential macronutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. Here are some key benefits of protein:
1. Muscle Growth and Repair
- Building Muscle: Protein provides the amino acids necessary for muscle protein synthesis, which is essential for muscle growth.
- Repairing Damage: After intense workouts, protein helps repair damaged muscle tissues, reducing soreness and accelerating recovery.
2. Weight Management
- Satiety: Protein-rich foods can help you feel fuller for longer, reducing overall calorie intake and aiding in weight management.
- Thermogenic Effect: Protein has a higher thermogenic effect compared to fats and carbohydrates, meaning your body burns more calories digesting and metabolizing protein.
3. Bone Health
- Bone Density: Adequate protein intake is associated with higher bone density and a reduced risk of fractures, especially important as you age.
4. Hormone Regulation
- Hormones: Protein is involved in the production and regulation of hormones, including those that control metabolism and appetite.
5. Immune Function
- Antibodies: Proteins are vital for the production of antibodies that help your immune system fight off infections and diseases.
6. Enzyme Production
- Metabolism: Enzymes, which are proteins, play a critical role in various metabolic processes, aiding in digestion and nutrient absorption.
7. Cell Structure and Function
- Cell Repair and Growth: Proteins are essential components of every cell in your body, supporting the repair, growth, and maintenance of tissues.
8. Energy Source
- Secondary Energy Source: While carbohydrates and fats are the primary energy sources, protein can also be used for energy, especially during prolonged exercise or calorie restriction.
9. Transport and Storage of Nutrients
- Transport Proteins: Proteins help transport nutrients like oxygen (hemoglobin) and vitamins (binding proteins) throughout the body.
- Storage: Some proteins function as storage molecules, holding onto essential nutrients until the body needs them.
10. Improved Hair, Skin, and Nails
- Keratin: Protein is a key component of keratin, which makes up your hair, skin, and nails, contributing to their strength and health.
11. Cognitive Function
- Neurotransmitters: Protein helps in the production of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain, supporting cognitive function and mood regulation.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
The amount of protein you need can depend on several factors, including your age, sex, weight, and level of physical activity. However, a general guideline for muscle growth is:
- Beginners: 0.8 – 1.0 grams of protein per pound of body weight.
- Intermediate: 1.0 – 1.2 grams of protein per pound of body weight.
- Advanced: 1.2 – 1.5 grams of protein per pound of body weight.
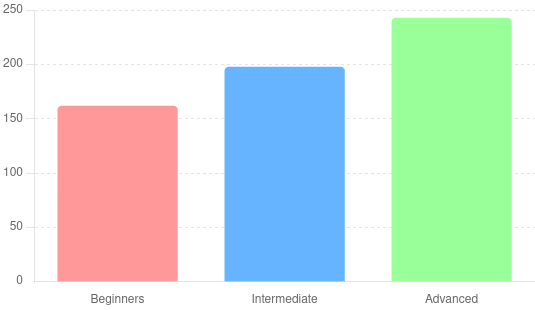
For example, if you weigh 180 pounds and are at an intermediate level, you should aim for 180 to 216 grams of protein per day.
Quality Over Quantity: Best Sources of Protein
Not all proteins are created equal. Here are some of the best sources of high-quality protein:
- Lean Meats: Chicken breast, turkey, and lean cuts of beef are excellent sources of complete protein.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, and other fatty fish are rich in protein and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Eggs: One of the most versatile and complete protein sources.
- Dairy: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and milk provide not only protein but also calcium.
- Plant-Based: Lentils, chickpeas, quinoa, and tofu are great for those following a vegetarian or vegan diet.
- Protein Supplements: Whey, casein, and plant-based protein powders can help you meet your daily protein goals conveniently.
Timing Your Protein Intake
When it comes to muscle growth, timing can be just as important as the amount of protein you consume. Here are some key times to prioritize protein intake:
Post-Workout
The anabolic window, or the period post-exercise when your body is primed to absorb nutrients, is crucial. Aim to consume 20-40 grams of protein within 30-60 minutes after your workout to maximize muscle repair and growth.
Throughout the Day
Spreading your protein intake evenly throughout the day can be beneficial. Aim for 20-30 grams of protein per meal, with snacks containing 10-15 grams of protein.
Before Bed
Consuming a slow-digesting protein like casein before bed can provide your muscles with a steady supply of amino acids throughout the night, aiding recovery and growth.
Common Myths About Protein Intake
Myth 1: More Protein = More Muscle
While protein is essential, more isn’t always better. Excessive protein intake can lead to unnecessary calorie consumption and strain on the kidneys. Stick to the recommended guidelines for optimal results.
Myth 2: Protein Supplements are Necessary
While supplements can be convenient, they aren’t necessary if you can meet your protein needs through whole foods. Prioritize high-quality food sources and use supplements to fill in the gaps.
Myth 3: Only Animal Protein is Effective
Plant-based proteins can be just as effective for muscle growth if consumed in adequate amounts and combined to ensure a complete amino acid profile.
Practical Tips for Increasing Protein Intake
- Plan Your Meals: Include a source of protein in every meal and snack.
- Meal Prep: Prepare protein-rich meals in advance to avoid missing your targets.
- Incorporate Protein Snacks: Keep high-protein snacks like nuts, yogurt, or protein bars handy.
- Experiment with Recipes: Find creative ways to include protein in your diet, such as adding protein powder to smoothies or baking.
High-protein meal suggestions
| Meal Type | Meal | Ingredients |
| Breakfast | Greek Yogurt Parfait | Greek yogurt, fresh berries, honey, granola, chia seeds |
| Breakfast | Egg and Avocado Toast | Whole-grain toast, sliced avocado, poached or scrambled eggs, cherry tomatoes, spinach |
| Breakfast | Protein Pancakes | Protein powder, oats, cottage cheese, eggs, banana |
| Lunch | Grilled Chicken Salad | Grilled chicken breast, mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, avocado, olive oil and lemon dressing |
| Lunch | Turkey and Cheese Wrap | Whole-grain wrap, sliced turkey breast, low-fat cheese, lettuce, tomato, mustard or hummus |
| Lunch | Lentil and Quinoa Bowl | Cooked lentils, quinoa, roasted vegetables, feta cheese, tzatziki sauce |
| Dinner | Baked Salmon with Asparagus | Baked salmon fillet, asparagus, quinoa or brown rice, lemon and dill sauce |
| Dinner | Beef Stir-Fry | Lean beef strips, mixed vegetables, brown rice or whole-grain noodles, soy sauce and ginger |
| Dinner | Tofu and Vegetable Curry | Firm tofu, mixed vegetables, coconut milk, curry paste, brown rice or quinoa |
| Snack | Cottage Cheese and Fruit | Cottage cheese, sliced pineapple, peaches, or berries |
| Snack | Protein Smoothie | Protein powder, almond milk or regular milk, spinach, banana, peanut butter |
| Snack | Hard-Boiled Eggs | Hard-boiled eggs, sea salt and pepper |
| Snack | Edamame | Steamed edamame, sea salt |
| Dessert | Protein Mug Cake | Protein powder, oats, egg whites, baking powder, cocoa powder |
| Dessert | Greek Yogurt with Honey and Nuts | Greek yogurt, honey, mixed nuts |
Here are some high-protein meal suggestions that can help you meet your daily protein needs:
Breakfast
- Greek Yogurt Parfait
- Greek yogurt
- Fresh berries
- Honey
- Granola
- Chia seeds
- Egg and Avocado Toast
- Whole-grain toast
- Sliced avocado
- Poached or scrambled eggs
- Cherry tomatoes
- Spinach
- Protein Pancakes
- Protein powder
- Oats
- Cottage cheese
- Eggs
- Banana
Lunch
- Grilled Chicken Salad
- Grilled chicken breast
- Mixed greens (spinach, arugula, etc.)
- Cherry tomatoes
- Cucumber
- Avocado
- Olive oil and lemon dressing
- Turkey and Cheese Wrap
- Whole-grain wrap
- Sliced turkey breast
- Low-fat cheese
- Lettuce
- Tomato
- Mustard or hummus
- Lentil and Quinoa Bowl
- Cooked lentils
- Quinoa
- Roasted vegetables (bell peppers, zucchini, etc.)
- Feta cheese
- Tzatziki sauce
Dinner
- Baked Salmon with Asparagus
- Baked salmon fillet
- Asparagus
- Quinoa or brown rice
- Lemon and dill sauce
- Beef Stir-Fry
- Lean beef strips
- Mixed vegetables (broccoli, bell peppers, snap peas, etc.)
- Brown rice or whole-grain noodles
- Soy sauce and ginger
- Tofu and Vegetable Curry
- Firm tofu
- Mixed vegetables (carrots, bell peppers, spinach, etc.)
- Coconut milk
- Curry paste
- Brown rice or quinoa
Snacks
- Cottage Cheese and Fruit
- Cottage cheese
- Sliced pineapple, peaches, or berries
- Protein Smoothie
- Protein powder
- Almond milk or regular milk
- Spinach
- Banana
- Peanut butter
- Hard-Boiled Eggs
- Hard-boiled eggs
- Sea salt and pepper
- Edamame
- Steamed edamame
- Sea salt
Dessert
- Protein Mug Cake
- Protein powder
- Oats
- Egg whites
- Baking powder
- Cocoa powder
- Greek Yogurt with Honey and Nuts
- Greek yogurt
- Honey
- Mixed nuts (almonds, walnuts, etc.)
These meals are not only high in protein but also balanced with other essential nutrients, making them perfect for supporting muscle growth and overall health. Enjoy!
Conclusion
Achieving muscle growth is a combination of proper training, adequate rest, and optimal nutrition, with protein playing a central role. By understanding how much protein you need, choosing high-quality sources, timing your intake correctly, and debunking common myths, you can maximize your muscle-building potential.
Join us at Promuscle Club to stay informed and motivated on your fitness journey. Happy lifting!